Pollination
What’s your favorite summer crop? If you love apples, melons, cranberries, asparagus, or broccoli, you should give your sun hat to our fuzzy, insect friends.
To germinate, these plants require the transfer of pollen from the male part of the flower (the anther) to the female part (the stigma). As bees move from flower to flower in search of nectar, they leave behind grains of pollen on the sticky surface, allowing plants to grow and produce food.
Wild plant growth
It’s not just farm-grown fruits and vegetables that rely on pollinators to thrive. Many species of wild plants depend on insect pollinators as well. Bees are responsible for the production of many seeds, nuts, berries, and fruit, which serve as vital food sources for wild animals.
Food source
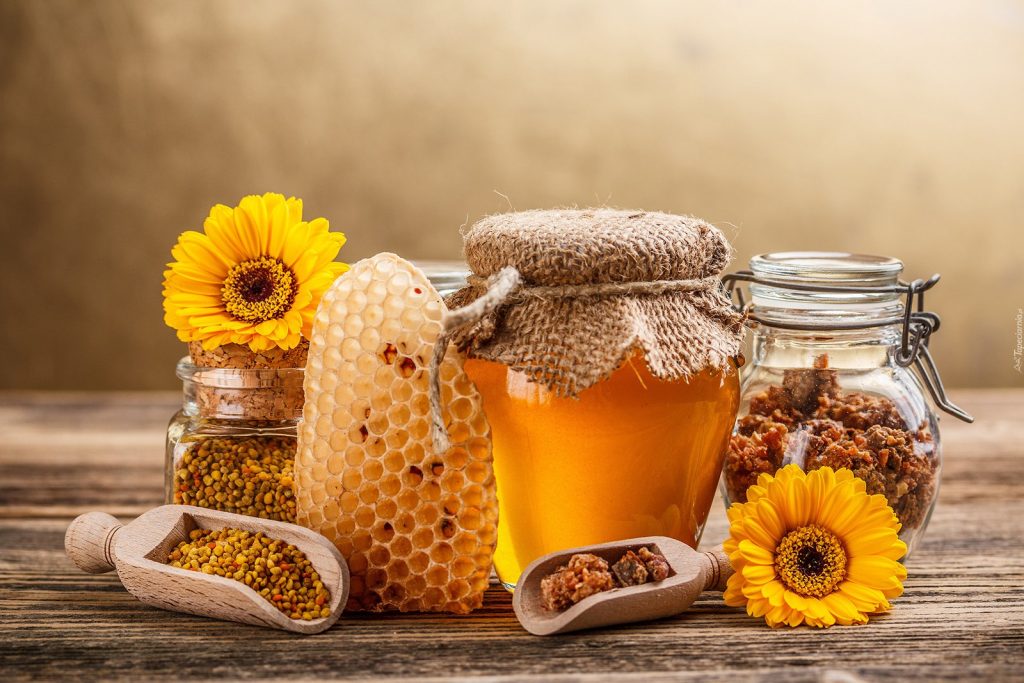
Bees produce honey to feed their colonies during the cold winter months. Humans have harvested honey for thousands of years, but we aren’t the only ones who consider it a sweet snack. Critters like birds, raccoons, opossums, and insects will raid beehives for a taste of nutritious honey (and bee larvae).
Wildlife habitats
Bees are known for their elaborate hives, but they also help build homes for millions of other insects and animals. Their role as pollinators is vital in the growth of tropical forests, savannah woodlands, and temperate deciduous forests. Many tree species, like willows and poplars, couldn’t grow without pollinators like bees.
Biodiversity
As pollinators, bees play a part in every aspect of the ecosystem. They support the growth of trees, flowers, and other plants, which serve as food and shelter for creatures large and small. Bees contribute to complex, interconnected ecosystems that allow a diverse number of different species to co-exist